
2022
Computer Characteristics and Operating Principles: A Simple Explanation
What are computer characteristics and how do computers work? The basic parts of a computer are the CPU, RAM, storage, input and output.
Computer characteristics are directly related to the purpose of computers. As everyone knows, computers and modern electronic computing devices work with information. Information technologies are a wide class of activities and disciplines related to the collection, storage, management, transmission, and protection of information. Different objects can interact with the information in different ways. Therefore, it is an abstract concept. Information devices use, transmit, and interpret information. The appropriate software can encrypt data for safe storage and communication. In order for the activities and disciplines related to information to be carried out, it must be structured. The basic information units (individual pieces of information) are called data.
Computer Characteristics
The characteristics of a computer system depend on its purpose. For example, a personal computer, a specialized manufacturing computer, a car computer, etc. Each of these listed types has several of the computer characteristics listed below.
Data processing speed
The computer characteristics evaluated by several factors.
Firstly, CPU speed. The processor processes the data at a certain clock frequency in the form of instructions. Higher frequency, higher number of instructions processed per unit time. The number of processor data buses is related to the volume of data processed per unit time. The presence of cache memory in the processor helps to process data faster.
As a second factor in the speed of the computer system is the volume and speed of the operating memory. The computer system equipped with more memory processes the data faster. A significant factor in overall performance is the speed at which data is transferred between the memory and the processor.
Accuracy in calculations and logical operations
The computer system must always make calculations with 100% accuracy.
Diligence and Versatility
A computer must perform many tasks or calculations with consistency and accuracy (multitasking).
Reliability
The computer must be reliable. To give a consistent result from repeatedly entered input data.
The operating system
The operating system acts as the main software installed on the computer system. The overall performance of the computer depends on its capabilities and condition. For example, whether it fully supports processor instructions; whether it has the necessary drivers for peripheral devices; whether it allows working with many processor cores (multithreading) at the same time.
Moreover, is it well written and optimized?
Data units
Data processing is a process of operations on data – collection, storage, conversion, protection, dissemination.
The concept of information technology is more general than the concept of data processing and includes the methods related to processing and application of data.
The information, in turn, is the result of data processing. Data organized in a usable form.
Data units presented with a binary number system
Today, the most widespread electronic computing machines work with data presented in a binary number system. With ones and zeros. The unit for measuring an amount of information is bit. The name comes from a transformation of the words binary digit.
Base units for data volume
- 1 bit = 0 or 1 basic logical data state;
- 1 Byte = 8 bits;
- 1 Byte = 8 bits;
- 1 KB (kilobyte) = 1024 b = 1000 ^ 1 Bytes;
- 1 MB (megabyte) = 1024 KB = 1000 ^ 2 Bytes;
- 1 GB (gigabyte) = 1024 MB = 1000 ^ 3 Bytes;
- 1 TB (terabyte) = 1024 GB = 1000 ^ 4 Bytes;
- 1 TB (terabyte) = 1024 GB = 1000 ^ 4 Bytes;
- 1 PB (petabyte) = 1024 TB = 1000 ^ 5 Bytes.
Computer architecture
In 1945, the mathematician John von Neumann, working at Princeton University in the United States, formulated the concept of consistent architecture with his assistant Goldstein. According to it, the computer consists of three main blocks CPU, Memory and Input / Output, interconnected by information buses.

The basic computer diagram
The functioning, structure, and implementation of computer systems are all described by a set of rules and procedures known as computer architecture. The following diagram shows the fundamental building blocks of a basic computer and how they interact. Red lines represent control flow, whereas black lines represent data flow. Arrows show the flow’s direction.
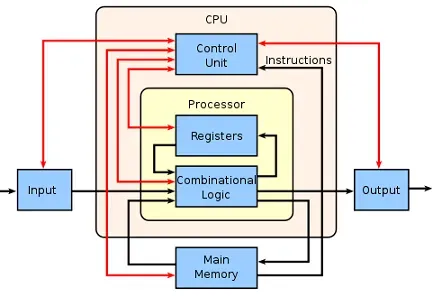
Hardware Computer Characteristics
Central Processor Unit
The CPU temporarily stores data and processes data. The processed data is divided into two types of operations: arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) and logical operations (comparison of values, connection of two or more words). Logical operations are also called Boolean operations.

The length of the machine word (the microprocessor processes several bytes, called machine word) there are several processor types. 16-bit Intel 8086, 32-bit PowerPC, 64-bit IA-64.
Classification according to the purpose of the CPU
– Specialized, usually built into control sites – cars, airplanes, electrical and electronic appliances, etc.
– Universal, the most popular representatives are personal computers. They are developed on the basis of universal microprocessors and their capabilities are constantly being improved.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
Memory is a device with which the processor directly exchanges information, repeatedly and at very high speeds during data processing. Memory stores data in the form of electrical signals in its cells. Voltages are interpreted based on three bands: If a device detects a voltage within one band, it is interpreted as logic 0, and if the device detects a voltage within another band, it is regarded as logic 1. This interpretation depends on the technology, supply voltage, and the ratio of active high to active low.
Conclusion
The computer characteristics, its organization, and optimization help optimize performance-based software products. For example, hardware support for a certain type of instruction in the processor itself can increase system performance for some tasks. In addition, technologies for processors, memories and other electronic devices are constantly evolving. Developments lead to more powerful and efficient computer systems. The Moore’s Law, states the number of transistors on new microprocessor models will approximately double every 18-24 months, and hence the computing power of the processors.
Check your computer characteristics with our Online PC Hardware Checker Tool.
Contact
Missing something?
Feel free to request missing tools or give some feedback using our contact form.
Contact Us